Advance Pricing Agreement
Advance Pricing Agreement: Advance pricing agreement (APA) have been introduced by the by finance act, 2012 by inserting section 92CC and 92CD. It came to effect from 1st July 2012. Rules 10G to 10T and 44GAAuthor Name: Gayathrisankaran
Advance Pricing Agreement: Advance pricing agreement (APA) have been introduced by the by finance act, 2012 by inserting section 92CC and 92CD. It came to effect from 1st July 2012. Rules 10G to 10T and 44GA
Advance Pricing Agreement
Advance pricing agreement (APA) have been introduced by the by finance act, 2012 by inserting section 92CC and 92CD. It came to effect from 1st July 2012. Rules 10G to 10T and 44GA have been introduced vide notification on August 30th 2012 to govern APA mechanism. Purpose of introduction of APA is mainly to resolve transfer pricing disputes.
EVOLUTION OF APA
The system of APA was first introduced in Japan in 1987.It was developed to ensure proper and smooth enforcement of transfer pricing regulation. United States Internal Revenue Service adopted APA system in 1991, subsequently Canada adopted it in 1994, Australia adopted it in 1995.China adopted it in 1998, UK and France adopted it in 1999.Germany adopted it in 2000.The system became a focus of global interest. In India APA agreement was introduced in 2012.
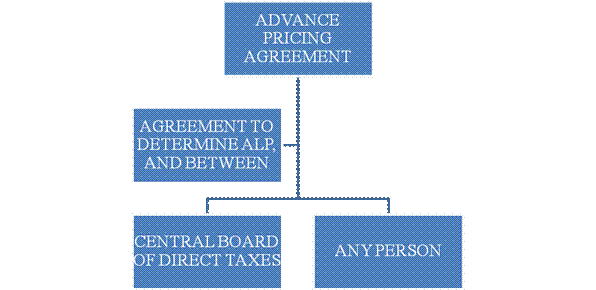
MEANING OF APA
An APA is the agreement between board and person, which determines in advance, arms length price or the manner of determination of arms length price or both, in relation to international transaction. Once Arm’s length price (ALP) calculation is determined by APA for an international transaction for a specified period, then arm’s length price will be determined only according to method mentioned in the APA.
An (APA) (or “arrangements”) as referred to by the OECD in its 2010 transfer pricing guidelines is “An arrangement that determines, in advance of controlled transactions, an appropriate set of criteria for the determination of the transfer pricing for those transactions over a fixed period of time”.
Term of an APA: Term of APA can be maximum of 5 years. Minimum time period is neither.
Mentioned neither in the Income tax act nor in the rules.
Types of APA: There are 3 types of APA. They are as follows:
• Unilateral APA
• Bilateral APA
• Multilateral APA
ALP DETERMINATION AND AUTHORITY
| Type of APA | Number of countries involved | ALP is determined by | Application of ALP is handled by |
| Unilateral | 1 | Competent authority of resident county | APA directorate |
| Bilateral | 2 | After the consultation with Two tax administration that have jurisdiction | Competent authority |
| Multilateral | More than 2 | After consultation with more than 2 tax administrations that have jurisdiction | Competent authority |
UNILATERAL APA
A unilateral APA is an one sided APA i.e the pricing is agreed with tax administration of home country while in the related parties jurisdiction, the related party will still have to undergo the routine litigation process. If Associated enterprises (“AE”) jurisdiction raises a transfer pricing adjustment with respect to a transaction or Issue covered by the unilateral APA, then the unilateral APA can be treated as the taxpayer’s filing and therefore eligible for MAP and adjustable, as opposed to an irreversible settlement. Considering the above, it is evident that the unilateral APAs do not reliably eliminate double taxation issue or might even create taxation gaps and therefore are less preferred by the taxpayers.
BILATERATERAL\MULTILALATERAL APA
These APAs ensure that the arrangements will reduce the risk of double taxation, will be equitable to all tax administrations and taxpayers involved, and will provide greater certainty to the taxpayers concerned. These APAs offer greater tax certainty and address the full scope of a transaction and are therefore are favored over unilateral APAs. When such agreements are possible, revenue authorities generally avoid entering into multiple unilateral agreements. However, the only downside of these APAs is that, there is high time-cost involved in concluding such type of APAs. These needs to be weighed against the benefits a taxpayer may achieve in his case.
Request for bilateral or multilateral APA can be accepted by Indian competent authority
• If mutual agreement procedure is present in the treaty between India and other country
• In case of international transactions leading to double taxation arising out of transfer pricing agreement
• If similar APA program exist in other country
SCOPE OF APA:
Applying for an APA for transactions is generally left to the discretion of the taxpayer. There is no statutory obligation for a taxpayer to cover all the related party or intercompany transaction in an APA, however, it is generally recommended to disclose all the inter-company Transactions proposed to be entered into by the taxpayer to the relevant tax authorities so that both the parties may discuss and come to a consensus to include such transactions. As the APA proposals are independent in nature and binding only on the person in whose case the agreement has been entered into and only in respect of the transaction in relation to which the agreement has been entered into.
The scope of an APA also states the time period for which the APA shall remain in force. In India APA can be entered for maximum period of five years with the option of renewal.APA entered for past transactions is called roll back APA. In India roll back APA cannot be entered. In India APA can be entered for present and futuristic transaction only.
APA FRAMEWORK IN INDIA:
Section 92CC of Income tax act deals about the structure of APA.
CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF SECTION 92CC
Applicability: APA can be entered by the board with any persons undertaking international transactions or Contemplating to undertake international transactions. International transaction’s meaning is dealt under section 92B of income tax act .According section 92B international transaction means
• A transaction between two or more associated enterprises.
• Either both or at least one of the enterprise should be non resident
• It should be in nature of
# Purchase, sale or lease of tangible property,
# Provisions of services,
# Lending or borrowing of money
# Any other transaction having beating on profits\income\losses\assets of such enterprise
• It includes a mutual agreement or arrangement between two or more associated enterprise for
# Allocation or
# Apportionment or
# Contribution to
# Any cost or expense in connection with any benefit, service or facility provided or to be provided to or more deemed enterprises.
• It also includes deemed transactions between non-associated enterprises as dealt under section 92B (2).After 2012 explanation was inserted by way of amendment which is applicable retrospectively from 2002. According to the explanation capital financing is an international transaction.
Vijai electrical ltd v ACIT
The assessee invested Rs. 21 Crores in the share capital of its overseas subsidiaries. The AO completed the assessment without making any transfer pricing adjustment.
Issue:
• Whether transfer pricing provisions is applicable to an investment in share capital of overseas companies?
• Whether Transfer pricing provisions is applicable to transactions where no “income” has arisen?
CIT DECISION:
The CIT revised the assessment u/s 263 on the ground that the transaction was an “international transaction” u/s 92B and that the AO ought to have referred the matter to the TPO to determine whether the investments were made at arm’s length. The assessee filed an appeal before the Tribunal in which it argued (i) that an investment in the share capital of another company was not an “international transaction” u/s 92-B and (ii) as there was no “income“, the transfer pricing provisions did not apply.
Decision: It was held by the Tribunal upholding the plea: An amount paid for investment in share capital of subsidiaries outside India is not in the nature of an “international transaction” as defined in s. 92-B.
Transfer pricing provisions are not applicable to transactions where there is no income In Dana Corporation & Amiantit International contrary view was held ,regarding applicability of transfer pricing provisions in Perot Systems & the series of judgments
Determination of arm's length price
The manner of determination of arm's length price referred to in sub-section (1), may include the methods referred to in sub-section (2) of section 92C or any other method, with such adjustments or variations, as may be necessary or expedient so to do.
Binding effect of APA:
According to section 92CC (5) OF Income tax Act, APA is binding both on tax authorities and person entering on APA. Once Arm’s length price is determined in APA, that price only will prevail for that specified transaction.
Not binding: APA not binding if there is a change in law or facts affects the agreement previously entered. The Board may, with the approval of the Central Government, can declare an agreement to be void ab initio, if any of the conditions is satisfied:
CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF SECTION 92 CD
Section 92CD deals about effect of advance pricing agreement. According to it
1. Compulsory filing of modified return: The taxpayer entering into an APA compulsorily must furnish modified return for the years to which APA applies within 3 months from end of the month in which APA comes into effect.
2. Modified returns should reflect only modification relevant to issues arising under the APA
3. Pending proceedings: In case of any pending assessment or reassessment proceedings at the time of filing the modified return, the same are to be finalized based on the modified return and the normal period of limitation for completion of the proceedings would be extended one year
4. Total income assessed base on modified return: In case of assessment or reassessment proceedings have been completed at the time of filing the modified return ,total income would need to be assessed or reassessed based on modified tax return within one year from the end of the financial year in which modified return is filed
5. Appeal can be filed: If any taxpayer aggrieved by the order of the assessment order of the assessment order passed in consonance of the modified return, can file for appeal with income tax commissioner.
Rules governing APA:
It is the rules which govern the working of APA mechanism. Rules 10G to 10T and 44GA govern APA mechanism. Let us examine few of these rules in detail
Critical assumption: meaning of critical assumptions is given under rule 10F (ii) of income tax rules. Accordingly it means also those assumptions which are so important, without which the parties to an agreement cannot enter into agreement. if critical assumption is changed, should be informed to the tax authorities at earliest possible. it will be revised or cancelled accordingly.
Processing of APA application: processing of application will be done as per 10K of income tax rules. Application can be rejected, if it is not in accordance with 10H of income tax rules.
Pre Filing Consultation:
This is a mandatory requirement in the process and not an option provided to the
Taxpayer. Additionally it involves a mandate of providing a lot of detailed information, with an option to keep the name of the taxpayer and its related entities ‘anonymous’. The pre-filing consultation is neither binding on the Board nor the taxpayer to enter into an APA.
APA team: The APA team in India would comprise of
• designated income-tax officers
• include experts in economic, statistics, law or
• Any other field as may be nominated by the DGIT
This is a positive and welcome step taken as to deal complex issue of transfer pricing require an overall insight of global business practice
WITHDRAWAL FROM THE APA PROCESS
APA regimes in other countries generally allow taxpayers a flexibility to withdraw an APA application at any stage of the process. Such regimes typically enable the taxpayers to withdraw from an APA application if the negotiated position is not acceptable or the taxpayer does not see a point in agreeing to an APA because of a change in business circumstances.
In case the taxpayer withdraws from an APA process, it should seek an assurance from the APA authorities that disclosures made during APA discussions should not be shared to regular revenue authorities responsible for transfer pricing audits and tax audits
Amendments to Application: The APA scheme provides for the amendment of the application by the taxpayer at any time before the finalization of the agreement, in case allowed by the DGIT / CA on account of non-changing of material facts and payment of additional fees if required.
# change in critical underlying assumptions
# change in such law other than that which renders it non-binding
# request from CA in the other country
REVISION OF APA
The revision order is required to be in writing citing reasons of revision required and the following additional noteworthy features:
# revisions can be initiated by the Board / DGIT/ CA/ taxpayer
# opportunity of being heard to be provided
# non-agreement by the taxpayer on the proposed revisions may result in cancellation of the APA
negative findings of the compliance audit by the TPO
# failure in timely filing of annual compliance report or filing with material errors
# non-agreement by the taxpayer on the proposed revisions may result in cancellation of the APA
# on account of fraud or misrepresentation of facts
CANCELLATION OF APA:
This is governed by rule 10Q.The order of cancellation is required to have the following essential features:
# in writing with reasons
# opportunity of being heard to be provided
# formal communication to the concerned Assessing Officer and the TPO
Renewal of APA: The renewal of APA is permitted under the new APA rules requiring all other listed processes of fees, application, etc. other the pre-filing consultation required in case of the original filling.
Annual Compliance Report: It is governed by Rule10O.An annual compliance report has to be furnished in quadruplicate to DGIT for each of the years covered in the agreement. One copy each would be sent by the DGIT to the CA India, to the Commissioner of Income Tax who has the jurisdiction over the income-tax assessment of the taxpayer and one copy to the TPO having the jurisdiction over the taxpayer filed within thirty days of the due date of filing the income tax return for that year, or within ninety days of entering into an agreement, whichever is later.
Compliance Audit of the APA: It is governed by rule 10P. The TPO having jurisdiction over the applicant is authorized to carry out the compliance audit of the APA for each of the year covered in the agreement and is required to furnish his report within six months from the end of the month in which the annual compliance report is received by him. It is provided that such covered transactions under the APA scheme would not be audited by the TPOs under the routine transfer pricing assessment procedure.
The compliance audit under the APA scheme is not a general feature seen globally and should be restricted to purely a monitoring procedure than a verification audit procedure.
ADVANTAGES OF APA:
i. Certainty: It gives certainty to taxpayer in assessing Arm’s length price. since the tax to be paid by the taxpayer is certain and known in advance it promotes foreign direct investment Another benefit of resorting to an APA is that the taxpayer and tax authority may agree to a methodology other than the prescribed methods for determining the arm’s length price, depending upon the commercial nature of the international transaction. This may be quite useful in scenarios where transfer price is set with pure commercial rationale. Tax-payer can negotiate an economic method to justify the set transfer price.
ii Avoids double taxation: due to bilateral and multilateral APA, risk of double taxation is reduced.
iii. Expert members in APA team: as APA members consist of experts in various field like law, statistics and economics it gives global insight to solve complex problems of transfer pricing arising out of international transaction.
iv. Free flow of information: APA can facilitate free flow of information, in a less confrontational atmosphere, between the taxpayer and tax authority(s) for the purpose of agreeing on a methodology which is legally correct and practically workable. Thus, the interaction between the taxpayer and tax authorities during the APA negotiation helps in a more objective review of the issues involved.
From the angle of tax jurisdictions APA may pave the way for increased foreign direct investment as it will help in boosting the confidence of the foreign investors by bringing certainty in the transfer pricing issues.
v. Easy for the startup enterprise:
APA may be particularly helpful in case of start-up enterprises. Start-up enterprises require set up time in initial phase of business. So in the initial years it may end up in making very low profit or even losses. So it will be hardship for the tax-payer if a transfer pricing adjustment is imposed on the enterprise on the criteria that the transaction is not at arm’s length. APA can address this situation by including a provision of term-test. Term test refers to testing of an international transaction over a period of time rather than examining it on year to year basis. This relieves the tax-payer from the hassles of transfer pricing compliance for every year and from potential litigations
DISADVANTAGES:
If critical assumption is wrong then it will create hassle:
All said and done in the praise of the APA it must be kept in mind that no good things come without sweat. APA if not implemented in the right manner dilute the advantages associated to it. The fulcrum of the entire mechanism lies on the critical assumptions regarding the future market conditions in determination of the price. If the assumptions are not precise it may result into much hassle for both the tax-payers and the tax authorities. For instance in the event of an economic slowdown the determination of arm’s length prices by the methods determined by the APA may not show proper results. Consider a situation where there is significant change in the economic characterization of the taxpayer. This may render the methods agreed in APA redundant. Either APA needs to be revised or a new APA needs to be entered. This lead to additional hassles for the tax-payer as it results in outflow of substantial time and money.
No time limit for revision:
The APA scheme in the Indian context has come out with the revision procedures but does not specify any time limit for the completion of the revision. Instead the scheme rolls out similar procedures for revision as in the time of entering into the original agreement. This leads to the consumption of additional time and efforts of the taxpayer
Initial cost is bit high:
Besides the initial costs and time involved in the initial stages of APA is huge. Only the large taxpayers can afford to enter into an APA. Experiences in most countries show that time for completion of an APA may range from 12-48 months. The time is on the higher side in completion of a bilateral APA. So the tax authorities have to divert a large number of resources otherwise earmarked for other purposes. Also in between the APA period tax administration may also have to divert a lot of resources to monitor whether taxpayers are complying with APA. Further, in case of non- compliance with the terms of an APA the entire costs and efforts in agreeing an APA may go into vain and the basic purpose behind an APA gets vitiated. Besides unilateral APA suffer from some characteristic weaknesses. A unilateral APA does not eliminate the risk of double taxation. It only brings certainty in the jurisdiction to which unilateral APA is agreed onto. Also the foreign competent authority is not likely to allow a corresponding adjustment arising out of an APA that is inconsistent, in its view with the arm’s length principle.
Confidentiality is not assured:
Confidentiality is also an important concern as important group policies and trade secrets are disclosed by the taxpayers to the tax authorities while entering into APA. The information shared with the tax authorities during the course of finalizing an APA needs to be handled with great amount of diligence. The information shared by a tax-payer while negotiating an APA may contain the group policy, pricing policy, future business predictions, revenue model which are of strategic importance to the MNE group. Sharing of these with the competitors can adversely affect the tax-payers market position.
There is a great concern among the industry about the possibility of ill-use of the data by the tax authorities. Tax authorities may use the information as potential comparable information against the tax-payers who have not entered into APA. With the Indian APA scheme comprising of no provisions regarding the confidentiality of tax-payers information, it remains a matter of serious concern for the taxpayers.
Besides there may come across a situation where tax authorities and tax-payers don’t reach a unanimous conclusion, This may lead to a waste of resources from both the ends.
Bird’s eye view of APA regime globally:
The principal of APA was introduced in other countries long ago. Countries like USA, Japan, UK, Canada and Australia have developed regime of APA. Let us have bird’s eye of APA in other countries:
| Country’s name | Year of introduction of APA | Pre filing |
Type of APA present | Filing fee | Time frame with in which APA concluded | Maximum term of APA |
| US | 1992 | mandatory | all three types is present | no filing fees | there is no time frame stated | five years |
| Australia | 1992 | mandatory | all three types is present | $5000 | there is no time frame stated | five years |
| Canada | 2004 | mandatory | all three types is present | no filing fees | there is no time frame stated | five years |
| China | 2005 | optional | all three types is present | no filing fees | there is no time frame stated | five years |
| France | 2005 | optional | all three types is present | no filing fees | there is no time frame stated | five years |
| Germany | 2004 | optional | Unilateral APA is present | filing fee is not specified | within 180 days APA should be concluded | 3 years |
| Italy | 1987 | optional | Unilateral and bilateral APA is present | filing fees is not specified | there is no time frame with which it should be concluded | 5 years |
| Japan | 2012 | optional | Unilateral | filing fee is not specified | Time frame is 60 to maximum of 120 days within which APA is concluded | maximum period of APA term is not specified |
| Luthanisia | 1991 | mandatory | all three types is present | $50000 for big business and | Time frame is not specified | 5 years |
| $22500 for small business |
Analysis: From above it can be ascertained that most countries which has time frame to conclude APA has unilateral type of APA, and the term of APA is shorter when it is compared with other countries. In some countries pre filing is not mandatory and fees are not specified. some countries do have roll back APA.
India has all types of APA and pre filing is mandatory.pre consultation will give the taxpayer the certainty of tax to be paid. This will boost FDI. The only disadvantage is there is no time frame fixed for concluding the APA. if it is fixed ,APA regime will be even working more better than the present.
CONCLUSION:
APA is introduced with the objective of resolving transfer pricing disputes .it is win win situation for both the taxpayers and for the government. Government point of view FDI is boosted. Taxpayer point of view amount of tax payable is certain. The constitution of APA team with expert from various fields will give overall insights to solve the complex issues of transfer pricing in a better way.
Suggestions: India’s APA regime is comparatively good when compared with other countries. Countries in which all 3 type of APA is present do not have time frame to conclude APA. If India having 3 types of APA specifies the time period to conclude APA the system would work in a much better way.
Since at times retrospectively tax is charged in India, roll back APA can be allowed only for those transactions which was not taxed earlier, but taxed later retrospectively.
Thus India’s APA regime acts like a bridge attracting foreign investments in one hand and generating revenue to government on the other hand.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
BOOKS:
• Dr. Girish Ahuja and Dr. Ravi Gupta, Income tax Act, 2012 edition CCH publishers.
• Dr. Girish Ahuja and Dr. Ravi Gupta, Income tax rules, 2012 edition CCH publishers.
• G.Sekar, direct tax –a ready reference eleventh edition, C. Sitaram & co ltd.
• Radika suri ,fundamentals of transfer pricing,2008th edition taxman
The author can be reached at: Gayathrisankaran@legalserviceindia.com
 |
This article has been Awarded Certificate of Excellence for Original Legal Research work by our Penal of Judges |
ISBN No: 978-81-928510-1-3
Author Bio: 3rd year School of excellence in Law
Email: gayathrisankaran@legalserviceindia.com
Website: http://www.
Views: 4410
How To Submit Your Article:
Follow the Procedure Below To Submit Your Articles
Submit your Article by using our online form
Click here
Note* we only accept Original Articles, we will not accept
Articles Already Published in other websites.
For Further Details Contact:
editor@legalserviceindia.com
File Your Copyright - Right Now!

Online Copyright Registration in India
Call us at: 9891244487 / or email at: admin@legalserviceindia.com
File Divorce in Delhi - Right Now!
File Your Mutual Divorce -Call us Right Now at: 9650499965 / or email at: tapsash@gmail.com
Lawyers in India - Search By City |
|||
|
Delhi Chandigarh Allahabad Lucknow Noida Gurgaon Faridabad Jalandhar Vapi |
Mumbai Pune Nagpur Nashik Ahmedabad Surat Indore Agra Jalgaon |
Kolkata Siliguri Durgapur Janjgir Jaipur Ludhiana Dimapur Guwahati Amritsar |
Chennai Chandigarh Hyderabad Coimbatore Eluru Belgaum Cochin Rajkot Jodhpur |

